Chemistry
Learning Track Courses
 Introduction to Chemistry (Senior Secondary)This course establishes the full scope of chemistry. It covers the formal meaning of the discipline, its real-world applications, its adverse effects, and the scientific method that underpins all chemical inquiry. It also provides an overview of chemical industries and the career paths available to chemists.
A correct understanding of chemistry's role is essential for scientific literacy. This course provides the foundational context for all future study, linking abstract principles to industrial processes, career opportunities, and their societal and environmental impact. It is the necessary starting point for a structured education in the chemical sciences.
By the end of this course, you will be able to define chemistry, outline the steps of the scientific method, describe the applications and negative effects of chemical processes, identify major chemical industries, and list the primary career opportunities available to a chemist.
This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1) beginning their formal study of chemistry. It provides the essential context required before proceeding to the study of matter, its properties, and the laws that govern its behaviour.
Introduction to Chemistry (Senior Secondary)This course establishes the full scope of chemistry. It covers the formal meaning of the discipline, its real-world applications, its adverse effects, and the scientific method that underpins all chemical inquiry. It also provides an overview of chemical industries and the career paths available to chemists.
A correct understanding of chemistry's role is essential for scientific literacy. This course provides the foundational context for all future study, linking abstract principles to industrial processes, career opportunities, and their societal and environmental impact. It is the necessary starting point for a structured education in the chemical sciences.
By the end of this course, you will be able to define chemistry, outline the steps of the scientific method, describe the applications and negative effects of chemical processes, identify major chemical industries, and list the primary career opportunities available to a chemist.
This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1) beginning their formal study of chemistry. It provides the essential context required before proceeding to the study of matter, its properties, and the laws that govern its behaviour.
This course establishes the full scope of chemistry. It covers the formal meaning of the discipline, its real-world applications, its adverse effects, and the scientific method that underpins all chemical inquiry. It also provides an overview of chemical industries and the career paths available to chemists. A correct understanding of chemistry's role is essential for scientific literacy. This course provides the foundational context for all future study, linking abstract principles to industrial processes, career opportunities, and their societal and environmental impact. It is the necessary starting point for a structured education in the chemical sciences. By the end of this course, you will be able to define chemistry, outline the steps of the scientific method, describe the applications and negative effects of chemical processes, identify major chemical industries, and list the primary career opportunities available to a chemist. This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1) beginning their formal study of chemistry. It provides the essential context required before proceeding to the study of matter, its properties, and the laws that govern its behaviour.
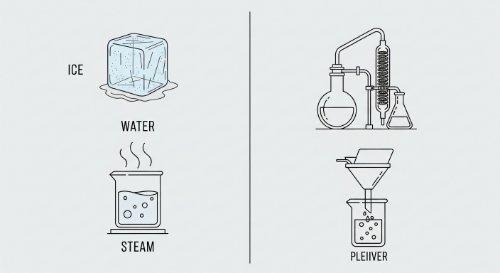 Introduction to Matter and Separation Techniques - Chemistry (Senior Secondary)This course provides a complete introduction to the classification of matter. It covers the fundamental distinction between elements, compounds, and mixtures, and the physical and chemical changes matter undergoes. The course culminates in a practical survey of the standard laboratory techniques used to separate mixtures based on the physical properties of their components.
An understanding of these concepts is essential for all practical chemistry. It provides the framework for classifying substances and the hands-on skills required to purify them. These techniques are used daily in research, industrial quality control, and environmental analysis to isolate and identify chemical substances.
By the end of this course, you will be able to differentiate between elements, compounds, and mixtures, distinguish between physical and chemical changes, and describe the principles behind standard separation techniques, including filtration, evaporation, distillation, sublimation, and chromatography.
This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1) and serves as the bridge between the theoretical introduction to chemistry and the study of its particulate nature. It provides the essential practical and conceptual knowledge required for all subsequent laboratory work.
Introduction to Matter and Separation Techniques - Chemistry (Senior Secondary)This course provides a complete introduction to the classification of matter. It covers the fundamental distinction between elements, compounds, and mixtures, and the physical and chemical changes matter undergoes. The course culminates in a practical survey of the standard laboratory techniques used to separate mixtures based on the physical properties of their components.
An understanding of these concepts is essential for all practical chemistry. It provides the framework for classifying substances and the hands-on skills required to purify them. These techniques are used daily in research, industrial quality control, and environmental analysis to isolate and identify chemical substances.
By the end of this course, you will be able to differentiate between elements, compounds, and mixtures, distinguish between physical and chemical changes, and describe the principles behind standard separation techniques, including filtration, evaporation, distillation, sublimation, and chromatography.
This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1) and serves as the bridge between the theoretical introduction to chemistry and the study of its particulate nature. It provides the essential practical and conceptual knowledge required for all subsequent laboratory work.
This course provides a complete introduction to the classification of matter. It covers the fundamental distinction between elements, compounds, and mixtures, and the physical and chemical changes matter undergoes. The course culminates in a practical survey of the standard laboratory techniques used to separate mixtures based on the physical properties of their components. An understanding of these concepts is essential for all practical chemistry. It provides the framework for classifying substances and the hands-on skills required to purify them. These techniques are used daily in research, industrial quality control, and environmental analysis to isolate and identify chemical substances. By the end of this course, you will be able to differentiate between elements, compounds, and mixtures, distinguish between physical and chemical changes, and describe the principles behind standard separation techniques, including filtration, evaporation, distillation, sublimation, and chromatography. This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1) and serves as the bridge between the theoretical introduction to chemistry and the study of its particulate nature. It provides the essential practical and conceptual knowledge required for all subsequent laboratory work.
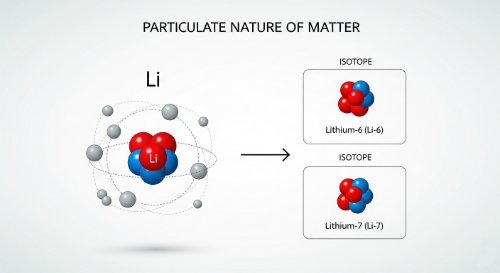 The Particulate Nature of Matter - Chemistry (Senior Secondary)This course provides a complete introduction to the building blocks of all substances. It formally defines atoms, molecules, and ions, and covers the core principles of Dalton's atomic theory. The course then details the modern model of the atom, including its constituent particles, and introduces the concepts of atomic number, mass number, isotopes, and relative atomic mass.
A correct understanding of the particulate nature of matter is the absolute foundation of all chemistry. It explains why elements and compounds behave the way they do and provides the framework for understanding chemical bonding, reactions, and stoichiometry. This is the microscopic viewpoint that makes sense of the macroscopic world.
By the end of this course, you will be able to define atoms, molecules, and ions, state the postulates of Dalton's atomic theory, describe the properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons, determine the atomic and mass number of any element, and explain the concept of isotopy.
This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1). It is the essential prerequisite for the study of the periodic table, chemical bonding, and the quantitative analysis of chemical reactions.
The Particulate Nature of Matter - Chemistry (Senior Secondary)This course provides a complete introduction to the building blocks of all substances. It formally defines atoms, molecules, and ions, and covers the core principles of Dalton's atomic theory. The course then details the modern model of the atom, including its constituent particles, and introduces the concepts of atomic number, mass number, isotopes, and relative atomic mass.
A correct understanding of the particulate nature of matter is the absolute foundation of all chemistry. It explains why elements and compounds behave the way they do and provides the framework for understanding chemical bonding, reactions, and stoichiometry. This is the microscopic viewpoint that makes sense of the macroscopic world.
By the end of this course, you will be able to define atoms, molecules, and ions, state the postulates of Dalton's atomic theory, describe the properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons, determine the atomic and mass number of any element, and explain the concept of isotopy.
This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1). It is the essential prerequisite for the study of the periodic table, chemical bonding, and the quantitative analysis of chemical reactions.
This course provides a complete introduction to the building blocks of all substances. It formally defines atoms, molecules, and ions, and covers the core principles of Dalton's atomic theory. The course then details the modern model of the atom, including its constituent particles, and introduces the concepts of atomic number, mass number, isotopes, and relative atomic mass. A correct understanding of the particulate nature of matter is the absolute foundation of all chemistry. It explains why elements and compounds behave the way they do and provides the framework for understanding chemical bonding, reactions, and stoichiometry. This is the microscopic viewpoint that makes sense of the macroscopic world. By the end of this course, you will be able to define atoms, molecules, and ions, state the postulates of Dalton's atomic theory, describe the properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons, determine the atomic and mass number of any element, and explain the concept of isotopy. This course is designed for senior secondary students (SSS 1). It is the essential prerequisite for the study of the periodic table, chemical bonding, and the quantitative analysis of chemical reactions.